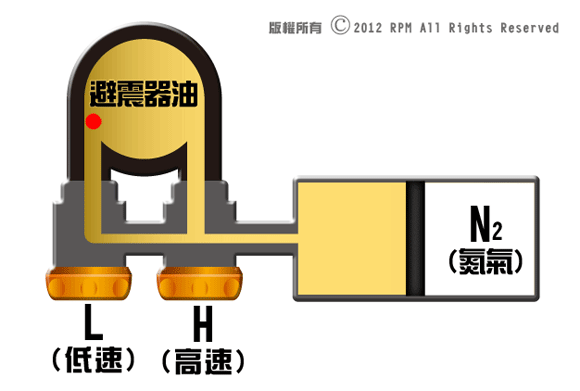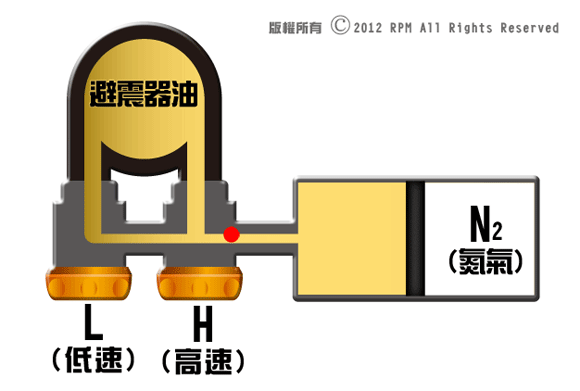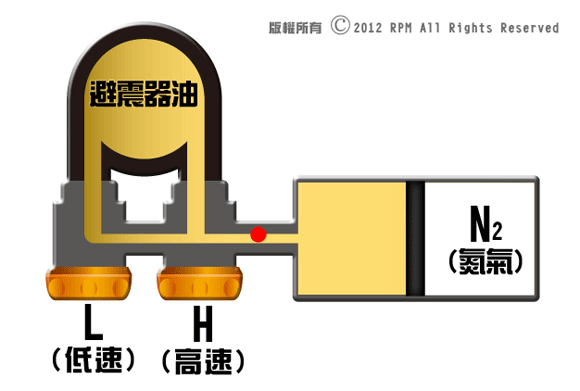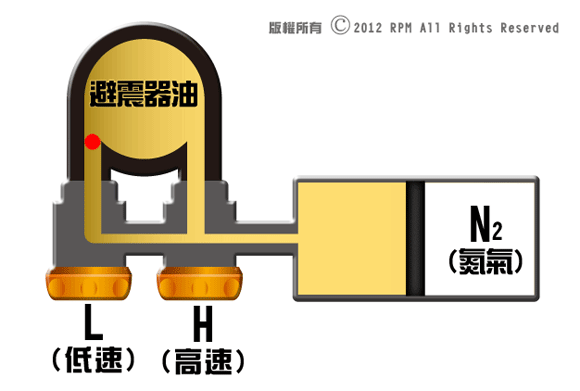
Simple shock
absorber:
Design with
no reservoir, with oil and gas mixture, shock absorbers will allow gas compress
simultaneously to balance the pressure within body tube. RPM body tube design with
gas-oil separation mechanism; although no difference in appearance and design
cost is higher, but you can effectively prevent the shock absorber oil mixed
with nitrogen at high pressure, avoid damper fade with short time period.
When shock
absorbers working, shock absorber oil flow through the piston within the
cylinder in between chamber A and chamber B, through piston shims, it creates
different level of damping resistance. When shock absorber compression and
rebound rapidly, shock absorber oil flow back and forth through different holes
on the Pistons, resulting in different compression and rebound damping effects.
Piston
with shims, control piston holes of opening and closing, due to oil flow speed
changing, lead to shock absorber compression and rebound at different speeds
and achieve stable performance.

Damper
adjustable shock absorber:
Shock
absorber interior mainly consists of a piston rod, piston, shims, oil seal, and
valve. In addition to the shock absorber oil viscosity, temperature and shims on
the piston hole opening and closing will affect the damping rate, and
damping-adjustable shock absorbers hard and soft control mainly determine through
the valve orifice size which is located on the axis of the piston rod, opening more
of the valve increases shock absorber oil flow, shock absorber is relatively
soft, and vice versa.
When shock
absorber receive equal amount of force, valve open bigger will create less
resistance, damper is softer, and vice versa.
In
General, shock absorber Hi/Low speed knob is often misinterpreted as vehicles
moving at a low speed adjust the low speed knob adjusting hi speed knob at high
speed, in fact, this is wrong. High speed correctly interpreted is not the
speed of the vehicle moving, but the shock absorber oil flow rate.
Hi/Low
speed damping principle is basically similar with rebound damping, are using
valve size to control shock absorbers of soft and hard damping rate, low speed
valve has two-way oil passage, it can flow in and out, but high-speed valve has
only one-way valve, only flow in, oil will then flow via low speed valve and
back to body tube.
Low
pressure oil flow, less resistance, L valve activate, H valve Closed (small
holes on pavement or gravel road)
High
pressure oil flow, L and H valve both activate (Pavement road surface with
large potholes)
When
vehicles travel in continuity of small pit hole surface, such as gravel road,
then shock absorbers device travel is small, oil flow speed is low, the high-speed
valve will not open, oil only circulate in low speed mechanism, when vehicles travel
on surface that has big hole or uneven pavement, then shock absorbers device travel
is big, oil flow speed become high, pressure is big enough to open high-speed
valve, oil will then flow through high-speed valve and low speed valve.
Gravel
road, shock absorber will actuated in small stroke, small, oil flow pressure is
low; Potholes can cause a sudden pressure rise, causes larger stroke, oil flow pressure
become high.
High
speed damper effect:
Low speed
compression damper-L is control with "continuous moving small travel of
piston rod", is in charge with range of piston rod travel, how much does it
effects the travel range? The answers is "Loading weight" and
"cornering" stability!
High-speed
compression damper-H is in control of the "sudden moving big travel of
piston rod" is in charge with range of piston rod travel, how much does it
effects the travel range? The answer is "holes on road surface"!
Hi/Low damper adjustment
instruction
High or low speed
damping adjustment adjust the damping is actually a very time consuming task,
the reason lies between high low speed mechanism affect each other, and
everybody's riding style are not the same, so that each rider’s preference
adjustments are not the same. Thus provides a simple way for your reference
below.
First of all,
please remember that clock wise direction click is hard adjustment, anti clock
wise direction is soft adjustment , this applies to Hi/Low compression adjustment.
Turn low speed
knob in clockwise direction to the end, high-speed anti counter clockwise to
the end. At this moment low speed mechanism is completely close, high-speed mechanism
is completely open. Intended to adjust the low-speed compression clicks,
because low speed is the easy adjustment, and is the most commonly used! Low
speed knob is close at this time, represents minimize of damping rate, with hardest
rate. So, when you encounter a pothole, your vehicle will vibrate like electric
massage chair, this is a normal phenomenon, do not panic! if you do not want
this, you can adjust low speed knob 5 clicks in counterclockwise direction,
then repeated the adjustment until you feel comfortable with the setting.
Taiwan road
surface is not in good condition, the adjustment test can be done anywhere
anytime, or test on unpaved asphalt pavement or gravel pavement! When you feel
the shock absorbers in "continuous motion and less travel" condition,
has obviously absorbed and actuation, represents the low-speed compression
damping adjustment is successful!
When
low-speed compression damping adjustment is completed, then it is time to
adjust the high-speed compression mechanism, the so-called high-speed damping is
in control of the "sudden actuation and dive deep stroke" when travel
over pavement "potholes". Or recommend way to find out the setting
tip is to ride faster on road, when it comes to "sidewalk" or "pavements
with potholes", apparently feel the jumps represent you must adjust the
high-speed compression damping. Actually high-speed compression adjustment is
not an easy task, because you must repeatedly test damping on poor road
condition, such as you can find a sidewalk, ride with certain and constant
speed, then you can obviously feel shock absorbers in "sudden actuation
and dive deep stroke" situation, the shock is obviously absorb and moving,
and not let you of shock absorbers bottom out, it represent you have completed high-speed
damping adjustment. Of course, we do not recommend this method to abuse your
ride!
Frequent Q&A
Q: Riding with low speed, feel vehicle vibrating
A: It means you will need to adjust
low speed compression more open flow .
Low speed compression too hard will slow down oil flow, and not able to
absorber vibration.
Q:
When riding with lower speed on potholes feel vibrating and bottom out?
A: It means you will need to adjust
High speed compression more open flow.
High speed compression too hard will slow down oil flow, and not able to
absorber vibration.
Q: When riding with high speed, feel vehicle
vibrating?
A: It means low
speed damper is necessary to increase.
Low speed
compression damping gap is too open, at high speeds, tire contact with pavement
movement is large and continuous! Lead to vehicle vibration and instability.
Q: When riding with
high speed, going over potholes and feel vehicle jump?
A: It means high
speed damper is necessary to increase.
High speed
compression damping gap is too narrow, lead to damper oil flow slow down, thus
unable to absorber sudden impact.
Q: When travelling
high speed corner, feel vehicle is vibrating and unstable?
A: It means LOW speed damper is necessary
to decrease.
A: It means low
speed damper is necessary to increase.
Low speed
compression damping gap is too open, damper oil flow too quick, lead to vehicle
vibration and instability.
Q: No matter how I
adjust, still cannot get correct hi/low setting, the vehicle is still unstable
and vibrating. Jumping and bottom out?
A: Before
compression damping adjustment, make sure spring preload and rebound are
correctly adjusted.
Although a
minor variation of spring preload, or rebound damping, it can also be correct
by adjust compression damping! But incorrect adjustment ~ such as adjustment of
spring preload is too tight, too loose. Or rebound damping rebound too fast,
too slow, and so on. Will lead to incorrect adjustment of high/low speed compression
damping, so if there are such problems, is not to do with your adjustment process,
but before compression damping adjustment, rebound adjustment and spring
preload adjustment are already adjusted incorrectly!
* Note:
prior to adjustment
of high low speed knob, you should first adjust spring preload and rebound damping
to appropriate setting, to adjustment that are unable to meet demand, regarding
detail rebound damping and spring preload adjustment mentioned on RPM website,
by the way, on the bottom comics provided allows riders to quickly review how!
伸側阻尼調整篇
RPM Website
Ruten Shop
http://class.ruten.com.tw/user/index00.php?s=rpm_shop
RPM Facebook Fans
http://www.facebook.com/1987rpm
RPM SUSPENSION Google+Fans
https://plus.google.com/u/0/108288935494178592737/posts
http://class.ruten.com.tw/user/index00.php?s=rpm_shop
RPM Facebook Fans
http://www.facebook.com/1987rpm
RPM SUSPENSION Google+Fans
https://plus.google.com/u/0/108288935494178592737/posts































Properly designed shock absorbers are essential for a smooth and controlled ride, preventing damper fade and ensuring consistent performance. For professional vehicle support and tyre services, visit tyre shop Dubai, where expert technicians provide reliable maintenance and repairs.
回覆刪除